- 1. Training
- 2. Websites and Website Information
- 3. Naming Conventions
- 4. Terminology
- 5. Shortcuts
- 6. ITSM Standards
- 7. Asana Tracking Standards
- 8. Personal UX Standards
- 9. SVG
- 10. Web Accessibility
- 11. Grace Link Recommendations
- 12. Helpful Links (WIP **)
- 13. Purpose of Meetings
- FERPA Basics - PRV802
- Review FERPA Information
- Protecting Social Security Numbers & Identity Theft Prevention - PRV804
- Protecting UF: Information Security Training
- PCard Refresher for Cardholders
- Compliance and Ethics: Doing your part for the Greater Good
- Maintaining a Safe and Respectful Campus
- Blue Man - Review of EM Protocols
- BEC Active Shooter - DEM827
- At-Risk for Faculty & Staff Kognito Training
- (Optional) Get eduroam on mobile device
Website Information
Slate
- Slate Emails
For forms that create emails, include captcha to reduce spam (However, this is not ADA friendly) - Test Slate Emails
-
You can now find two generic email templates in the Templates/ Email folder located in Slate. One version includes a placeholder for a banner image, the other version does not.
To change the image, button text, or hyperlink: simply double click on the image or button and enter in your new name (text), link text, etc.
Michael Merritt
Here are the links:
- Getting Started w/ Portals
-
Questions to ask client when building portal
- What is the overall goal of the portal?
- Who are its users?
- What actions must the users take within the portal?
- What must a user see on the portal?
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
- camelCase for variables, CSS classes and smaller-scoped items
- camelCaseExample
- PascalCase for globals, constants and classes that are objects (programming)
- ClassForCodeReuse
- underscores for images/media
- underscore_example.jpg
- dashes for filenames/folders/within CSS frameworks
- filename-or-folder-example
- EM
Container: Box that holds content in a mockup, prototype, webpage, etc.
Mockup: A draft visual representation of a design
Yield: Period in which students get accepted and decide on where to go to university
Specialized Terms:
-
Designers
- Hyphen
Never split words with hyphens
- Leading
Leading, or line-height, should be smaller on
pelements if possible - Specs
A design with exact measurements and colors defined and listed for reference
- Orphan
~~~ ~~~ ~~~ x - Runt
x ~~~ ~~~ ~~~ ~~~ - Widow
x ~~~ ~~~ ~~~ ~~~
- Hyphen
- Web Developers
- Signifiers/Affordances:
These are indicators that show users how to interact with new objects/situations
- Signifiers/Affordances:
-
| Windows | Web Browser | Xd | Zoom | VS Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Screen RecordWin + Alt + R |
Recover TabCtrl + Shift + T |
Scroll HorizontallyShift + Scroll |
Hide Bar (for remote IT help)Ctrl + Alt + Shift + H |
Open all files/folders from current directory in VS Code from Command Linecode . |
Screen CaptureWin + Shift + S |
Select items over areaShift + Click/Drag |
Microphone ToggleAlt + A |
Replace in FilesCtrl + Shift + H |
|
Narrator(SR)Win + Ctrl + Enter |
Video ToggleAlt + V |
Save all modified filesCtrl + Alt + S |
||
| Move Window Using Keyboard 1. Alt + Space2. M3. Arrow Keys4. Enter/Return to finalize |
Share Screen PromptAlt + S |
| Action | Script | Description |
|---|---|---|
| element-bkgd-5% | javascript: document.querySelectorAll("*").forEach(element => element.style.background="rgb(0 0 0 / 10%)"); |
Check bounds and distance b/w elements |
| design-mode-on | javascript: document.designMode="on"; void 0; |
Make document editable. Click and type. |
| get-inner-dimensions | javascript: void(0); alert(`Width: ${innerWidth}\nHeight: ${innerHeight}`); |
Get inner width and height |
| scroll-to-top | javascript: window.scrollTo({ left: 0, top: 0, behavior: "smooth" }); |
Scroll to top smoothly |
| scroll-to-bottom | A: javascript: window.scrollTo({ left: 0, top: document.body.scrollHeight, behavior: "smooth" });B: javascript: window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight || document.documentElement.scrollHeight); |
Scroll to bottom smoothly Version B is for the 2015 cross-platform version |
| remove-specific-cookie | javascript: document.cookie = 'cookie_key=; Max-Age=0; path = /; domain=.domain.ending'; |
CUSTOMIZABLE: Remove a specific cookie from your browser You must replace the cookie_key and .domain.ending with the correct values |
| activate-targeted-events | javascript: document.querySelector("SELECTOR").click(); |
CUSTOMIZABLE: Activate targeted events quickly |
flowchart LR
A([Detect]) --> B[Record];
B --> C{Classify};
C -.-> D[Incident];
D -.-> E[Investigate];
E -.-> I[Resolve];
C -.-> F[Request];
F -.-> G[Fulfill];
G -.-> I[Resolve];
I --> J([Close]);
| Low Impact | Medium Impact | High Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Urgency | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Medium Urgency | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Low Urgency | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Impact: Number of users/items affected/influenced
Urgency: Based on time until significant impact
| Category | Expectation |
|---|---|
| Task | Type(scope): Subject/Change needed |
| Assignee | Auto-populated |
| Due Date | Set by whom? |
| Priority | Monochromatic/How many levels? |
| Task Progress | Color-coded/Words used? |
| Related Branch | Git Branch being used |
| Job Type | This can be discussed. Current examples are Accessibility, New Page, Housekeeping, Content |
| Requested By | This can be auto-populated with a form |
- Priority: Current use is
- 🟨:Low
- 🟧:Med
- 🟥:High
- Task Progress: Current use is
- 🟦: In Queue
- 🔲: In Progress
- 🟨 (lighter tone): Waiting/On Hold
- 🟧: Revisions Requested
- 🟥: Ready for Review/On Test Site
- 🟩: Completed/Published
Nav
Confirmations Needed:
- Submenu/Search expands on click if collapsed
- Submenu/Search collapses on click if expanded
aria-expandedvalue matches these states- Keyboard navigation from these items does not close the item unless another item is focused
- Clicks outside button and menu/form close the item
Outbound Icons
Confirmations Needed:
- Outbound Icons accompany aria-label's announcing link is outbound
- When link is in nav/sidenav, icon is aligned right and vertically centered
- When link is a button, icon is aligned 4px to the right and baseline (vertically aligned icon bottom and text bottom)
Common svg commands for paths
| Letter | Command | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| M | Move To | M x y (or) m dx dy |
| L | Line To | L x y (or) l dx dy |
| H | Horizontal | H x (or) h dx |
| V | Vertical | V y (or) v dy |
| Z | Close Path | Z (or) z (no difference) Draws straight line from current point to first point in path. Doesn't need to be at end of path. |
| C | Cubic Curve | C x1 y1, x2 y2, x y (or) c dx1 dy1, dx2 dy2, dx dy |
| Q | Quadratic Bezier Curve | Q x1 y1, x y (or) q dx1 dy1, dx dy |
| S | Several Curve | S x2 y2, x y (or) s dx2 dy2, dx dy |
| A | Arc (7 params) | A rx ry x-axis-rotation large-arc-flag sweep-flag x y (or) a rx ry x-axis-rotation large-arc-flag sweep-flag dx dy |
Notes
- Uppercase letters are absolute. Lowercase letters are relative.
- Commas and spaces are optional (relatively).
- You can also drop the command letter if the next command is the same as the previous.
- If you want to change svg position on hover, use the exact same number of points.
Hover Effect Example
```html
<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100">
<path d="M10,10 Q50,20 50,50 T90,90" />
</svg>
```
```css
svg:hover path {
d: path("M10,10 Q80,20 50,50 T90,90")
}
```
Extra Information
- As an alternative, a plugin like GreenSock is able to smoothly morph an svg from one to another.
- SVG Conversion Utility to ALL Relative or ALL Absolute
Helpful when altering SVG code - SVG Animation w CSS
Informal precursor to using JS-based SVG animations - SVG Draw Line Animation w JS
Use JS to find path length for use in effects
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.2
- WebAIM Contrast Checker
Manual checks for color contrast issues - Chrome Color Contrast Analyzer
Extension with explanation on use - Color Blindness Filter Checker
Check ADA, CTA effectiveness and Gradient use - Web Accessibility Compliance Consultants Blog
- Great Color Branding Guide from UCLA
- Windows Narrator Keyboard Shortcuts
Narrator keyboard commands and touch gestures page via Windows Support - Cross Browser Environments and Screenreaders
Considerations for accessibility-first development and screenreaders - PDF Accessibility from WebAIM
- Helpful Walkthrough for InDesign Accessibility Tools and Use & Adobe InDesign Accessibility Documentation
- Access UF Training Sessions
Access some accessibility training through UF - Training Ideas for Accessibility at UC based on Job Filters
Access categories based on job to preview directions of study
- Beta ADA.gov Website
Official Beta for ADA linking to extra resources - Web Accessibility Under Title II of the ADA
ADA State and Local Toolkit - Web Accessibility Standards: ADA, Section 508 and WCAG
Understanding web accessibility standards - Font Size Change in Browser for Users
See how people use resizing to view content better - Parallax Effects and Accessibility
Read why not to use parallax and possible usable variants - Images and SVG's and Accessibility
Different methods for making these elements accessible - Decent Article on Accessibility
- Grid and Check accessible animations
- Accessiblity and Animations
- Blog on Accessibility and CSS & Lobotomized Owl Selector
Key Component: Action Plan
Now you know that some types of content and format on webpages can pose barriers for people with disabilities. The next steps are to develop an action plan to fix web content that is currently inaccessible and implement procedures to ensure that all new and modified web content is accessible. The website accessibility checklist included in this section helps you assess what needs to be done.
A well-designed action plan would include the following steps:
- Establish, implement, and post online a policy that your webpages will be accessible and create a process for implementation.
- Ensure that all new and modified webpages and content are accessible.
- Check the HTML of all new webpages. Make sure that accessible coding is used.
- Make sure that websites are designed so they can be displayed using the color and font settings of each visitor’s browser and operating system.
- If images are used, including photos, graphics, scanned images, or image maps, make sure to include a text equivalent, by adding “alt” tags or long descriptions, for each.
- If you use online forms and tables, make those elements accessible by labeling each control (including buttons, check boxes, drop-down menus, and text fields) with a descriptive HTML tag.
- When posting documents on the website, always provide them in HTML or a text-based format (even if you are also providing them in another format, such as PDF).
- Develop a plan for making your existing web content accessible. Describe your plan on an accessible webpage, and encourage input on how accessibility can be improved. Let visitors to your website know about the standards or guidelines that you are using to make your website accessible. When setting timeframes for accessibility modifications to your website, make more popular webpages a priority.
- When updating webpages, remember to ensure that updates are accessible. For example, when images change, the text equivalents in “alt” tags and long descriptions need to be changed so they match the new images.
- Ensure that in-house staff and contractors responsible for webpage and content development are properly trained. Distribute the Department of Justice technical assistance document “Accessibility of State and Local Government Websites to People with Disabilities” to these in-house staff and contractors on an annual basis as a reminder. This technical assistance document is available on the ADA Home Page at www.ada.gov.
- Provide a way for visitors to request accessible information or services by posting a telephone number or email address on your home page. Establish procedures that ensure a quick response to users with disabilities who are trying to obtain information or services in this way.
- Periodically enlist disability groups to test your pages for ease of use; use the feedback they provide to increase the accessibility of your website.
- Ensure that there are alternative ways for people with disabilities to access the information and services that are provided on your website. Remember, some people may not have, or be able to use, a computer.

- Usable: it means the design, structure, and purpose of the product is clear and easy to use. As you evaluate a product for usability, you can ask questions like: Is everything in the design easy to find? Is the design’s functionality easy to understand? Can users accomplish specific tasks within the design?
- Equitable: it means a design is helpful to people with diverse abilities and backgrounds. In other words, the product’s design addresses the needs of a diverse audience and ensures a high-quality experience is delivered to all users regardless of background, gender, race, or ability. Equity means providing people with the tools they need to accomplish their goals and support improved quality of life. Are the needs of a diverse group of users considered? Does the product’s design address the needs of traditionally underrepresented and excluded groups?
- Enjoyable: it means the design delights the user. The design reflects what the user may be thinking or feeling and creates a positive connection with them. Are there aspects of the design that consider the user’s feelings? Does the design inspire delight in the user? Does the design keep the user engaged throughout their experience?
- Useful: that means it solves user problems. In other words, the design intentionally solves a user problem that the designer has identified. It’s important to note that, while similar, useful and usable have different meanings. Does the design add value to the user’s experience? Does the design solve a problem for the user? Does the design help the user achieve a specific goal?
- Assets:
- Everything from the text and images to the design specifications, like font style, color, size, and spacing
- Information architecture:
- The framework of a website or how it’s organized, categorized, and structured
- Prototype:
- An early model of a product that demonstrates functionality
- UX research:
- Understand users and learn about their backgrounds, demographics, motivations, pain points, emotions, and life goals
- Wireframe:
- An outline or a sketch of a product or a screen
- Do my users have impairments or disabilities to consider–whether temporary, situational, or permanent?
- How familiar are my users with technology?
- How are my users accessing the product or service?
- Where and when are my users accessing the product or service?
- Have I considered all my potential users?
What is user research, and what's its purpose?
-
A platform is the medium that users experience your product on. Some common platforms are:
- Desktop computers
- Laptop computers
- Mobile phones
- Tablets
- Wearables, like smart watches
- TVs
- Smart displays
- Concerns for these experiences would be Screen Size, Interaction, Content layout and Functionality
- Accessibility:
- The design of products, devices, services, or environments for people with disabilities
- Alternative text (alt text):
- Text that helps translate something visual, such as an image or graph, into a description that can be read by screen readers
- Brand Identity:
- The visual appearance and voice of a company
- Call-to-action (CTA):
- A visual prompt that tells the user to take action, like to click a button
- Color modification:
- Features that increase the contrast of colors on a screen, like high-contrast mode or dark mode
- Design Sprint:
- A time-bound process, with five phases typically spread over five full 8-hour days. The goal of design sprints is to answer critical business questions through designing, prototyping, and testing ideas with users. Are there many potential solutions to your design challenge? Does a design challenge require people from cross-functional teams to weigh in? Is the design challenge's scope wide enough for a sprint?
- Design Thinking:
- A UX design framework that focuses on the user throughout all five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
- Sprint Brief:
- A document that you share with all your attendees to help them prepare for the sprint
Understand > Ideate > Decide > Prototype > Test
Each phase lasts a day
Resource: Google Design Sprint Kit
User research > Call in the experts > Find the right space > Gather supplies > Establish sprint rules > Plan introductions > Post-sprint planning
A sprint brief is shared with attendees and includes the following:
-
Sprint challenge/Challenge item
- What is the challenge that you want to solve in the sprint?
-
Four things that make a great challenge:
- Challenge is something real the team needs to deliver
- It's stated in an inspiring way - something to solve for
- It's clear/concise
- It includes a time frame
Key Deliverables
A few tips for deliverables
- Aim for the highest quality deliverables possible. Polished digital work, videos, and interactive prototypes are better than sketches.
- List all platforms that need to be designed for - e.g., web, mobile, tablet/physical product + website/environment
Logistics
- Where?
- When?
- Who? (list at end of doc - bookmark)
- Sprint Leader (established before brief created)
- Approvers: People who sign off before launch (ex. internal stakeholders, etc.)
Resources:
- For short term sprints: Assignment development team, if any (ex. engineering team)
- For long-term / vision sprints: Plan to secure resources
Project Overview
- Current state of project - what's been created already?
- Roadblocks - what stands in our way?
- Early wins, if any. - Has our team demonstrated any wins or learnings in the space already?
- Estimated launch plan - when is projected launch for piece being designed? What is this likely to look like at launch? (Include list in challenge statment as well)
- 5 Day Schedule: Specific hour by hour even to the 5 minute increment and should include break times
- You should have a prompt that guides your research - i.e. Sharpen prompt. Think through your audience and identify their unique needs/problems and how your product might solve these problems. Therefore, assure they are clear and focused on the problem your portfolio project is aiming to solve. You should have 2-5 research goals drafted.
- Define your target audience: Include a diverse but targeted group to get the best data. Note 3-6 different characteristics. Think about demographics like location, age and career.
- Write interview questions: These questions are the foundation for feedback later on. These can be adjusted as the portfolio project progresses. Draft 4-7 questions and be sure to follow best practices and avoid biases.
Use questionnaire or some form of gathering information to acquire data on pain points and interests of target audience.
- Understand the project scenario and customer types.
- Create personas based on a combination of attributes from a group of users with similar needs. Personas should be representative of key user groups.
- Consider the following while creating personas
- Demographic information: Did the demographic information match the persona characteristics given in the scenario?
- Quote: Were you able to imagine a quote that is relevant to the persona and the background you’ve built for them?
- Goals/frustrations: Were you able to align the goals and frustrations with the persona and the activity scenario?
- Brief story/scenario: Were you able to give more information about the persona, tying in their goals and frustrations, as well as their quote?
- Image: Did you include a picture or avatar representing the personas for your activity?
| Webpage | Reason |
|---|---|
| https://app.asana.com | Project management, organization and tracking |
| https://my.ufl.edu/ps/signon.html | Your UF Employment Related Resources |
| https://admissions.ufl.edu/ https://registrar.ufl.edu/ https://ufonline.ufl.edu/ https://em.ufl.edu/ https://veterans.ufl.edu/ https://www.sfa.ufl.edu/ |
Webpages related to what we do |
| https://my.admissions.ufl.edu/manage/ | Slate - Customer Relationship Management |
| EM Photoshelter UF General Photoshelter |
Personal bank of photos and most general photos pulled from photoshelter The UF-wide photoshelter is where they should be updating with more photos |
| https://webaim.org/resources/contrastchecker/ | Contrast Checker for ADA Compliance |
| https://www.flaticon.com/ | A database of icons used in design |
| https://www.toptal.com/designers/htmlarrows/ | Another icon database |
| https://identity.ufl.edu/color/ | UF's Color Branding |
| https://marcom.ufl.edu/.../.../model-releases/#release | Photo Model Release Form |
| Tools | Inspiration | Understanding Developers |
Further Reading | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Understanding HTML Heading Elements Line Typography Vocab and Visuals |
Design
- Image Optimization Perspective
Info on optimizing images for web - Color Palette Generator*
Tool to randomize a color palette - Expand Palette on One Color
Tool to expand palette based on input - Color Mixer
Tool for mixing colors - Behance
Creative network for showcasing and discovering creative work - Mobile First Design - Article by Adobe
Advantages and considerations for UI when building mobile-first - Difference Between Splash and Landing Pages
- Google UX Design Cert Review
Gives times for predicted amounts spent as well as summaries - Offline Considerations and UX Design
Perspective on web navigation for individuals with limited connectivity - Products that address pain points
- Image Grid Examples/Thoughts
- Color Fundamentals - Differences b/w RGB, CMYK, CMYKOGV, and SPOT Colors
- Colors for the Web: Suggested CSS4 Standards
- Heuristic Evaluation and Interaction Design
- Add Accents to Letters on Windows
- Line Readability and Character Count
- Using Êg to get actual height of a line
- Interactive Guide to Color and Contrast
- Lo-fi Wireframe Kit - Figma
- Future: Creative Asset Review Tool
- Text Spacing and Accessibility
- Wireframes in XD
- Fun Bad UX Example
Development
-
Regex and Regex tests: Regex 101 or Regexr
- Examples of possibly helpful syntax: (<!) syntax is negative lookbehind and (?!) syntax is negative lookahead
-
HTML URL Encoding Reference
Possible for API calls with input text -
Squoosh
Make image files smaller so they load faster (not necessary if using Image Optimizer on macOS) -
Lorem Picsum
Populate with random image with specified measurements -
Image Optimization Perspective
Info on optimizing images for web -
Git Stash Explained
Quick code/example on stash use -
Approximate Hex Color to Filter for SVGs
Inaccurate but free approximation for color to filter use on SVGs -
Styling svg use Content
Tips on using svg with css, specifically using svg use -
Fixing Focus Outlines
Correct the blob shape on focus outlines -
Oopsie: Remove sensitive data from repo - GitHub and Stackoverflow responses about removing with git rebase -i <commit_id>
-
Web Accessible Nav Types from W3
Explore for what is needed at time -
Explaining Web Caching to Clients
Brief overview of caching -
Absolute/Float Positioning in Relation to WYSIWYG Editors - for Legacy Updates
-
Force Browser to Reload CSS/Styles by Changing link tag URL
- Example:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/css/stylesheet.css?v=1" />
- Example:
-
- Use
Ctrl + F5to Clear Cache Memory in a Forced Refresh
- Use
- deno and npm: Node Compatibility Library
- Input w RegEx and ReactJS
- SQLite Installation - Mac
- SQLite Documentation/Download
- Bash Aliases
- Duplicate VSCode Environment
- Convert Static to React (not recommended)
- jekyll/hugo/11ty may be better for these circumstances to assure performance stays optimal
- 11ty Documentation
- 11ty 3 min Basic Tutorial
- 11ty Tutorial - Kevin Powell
- Lazy load images
- Fully CSS Accessible Tested Dropdown Nav
- Swiper
- JS Node ipdata.co
- Custom Reporting
- Tracking Device Orientation
- Google Analytics Alternative: Matomo (100% data ownership)
- GitLab - DevSecOps Platform: Alternative to GitHub
- QRCode Monkey - QR code generator
- Google Analytics Campaign URL Builder
- Decide on main campaign
- (optional) Use campaign name and year for naming convention
- Input URL to be used in tracking
- Use identifier for ID (see Step 2)
- Identify source (important)
- (optional) Reference marketing medium (or use source name)
- (optional) Campaign name can be the ID (see Step 4) if the ID is readable
- (optional) Fill out other fields
- Record the Generated Campaign URL
- (optional) Use Generated Campaign URL on a QR code generator page to tie the campaign to a QR code
- (optional - QR code) Decide/use pixel size based on medium (print/web/etc)
- Recursion
- Markdown Editing
- Understanding Recursion Post
- TLDR: The general recursion function is recurse() { doWeStop() || recurse(); } considering in most languages the "or" operator short-circuits when its first operand is true
base64convert function
function base64convert (files) {
console.clear()
const reader = new FileReader()
reader.onload = (e) => {
console.log(e.target.result)
}
reader.readAsDataURL(files[0])
} @font-face {
font-family: 'myfont';
src: url("<>");
}
base64 in font-face
@font-face {
font-family: 'gentonabook';
src: url(data:application/font-woff2;charset=utf-8;base64, USEBASE64HERE ) format('woff2'),
url(data:application/font-woff;charset=utf-8;base64, USEBASE64HERE) format('woff');
font-weight: normal;
font-style: normal;
}
https://www.elated.com/understanding-permissions/ https://zapier.com/blog/what-are-webhooks/
Webhooks
Note: Webhooks typically are used to connect two different applications. When an event happens on the trigger application, it serializes data about that event and sends it to a webhook URL from the action application—the one you want to do something based on the data from the first application. The action application can then send a callback message, often with an HTTP status code like 302 to let the trigger application know if the data was received successfully or 404 if not.Zapier
- URL
- Specifies where you want the data to go
- Body
- Contains the info/data you want to send
- Header
- Specifies how you want the info to be formatted
- Request
- Specifies the actions of the action app
Tip: The most common requests are GET, POST, PUT and DELETE
⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- FOLLOWING AREA IN PROGRESS -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔ -- -- -- ⛔
Workflow
- Remember:
git fetchandgit pullfrequently
Mermaid Documentation Flowchart
graph TD;
A-->B;
A-->C;
B-->D;
C-->D;
Sequence Diagram
sequenceDiagram
participant Alice
participant Bob
Alice->>John: Hello John, how are you?
loop Healthcheck
John->>John: Fight against hypochondria
end
Note right of John: Rational thoughts <br/>prevail!
John-->>Alice: Great!
John->>Bob: How about you?
Bob-->>John: Jolly good!
Gantt Diagram
gantt
dateFormat YYYY-MM-DD
title Adding GANTT diagram to mermaid
excludes weekdays 2014-01-10
section A section
Completed task :done, des1, 2014-01-06,2014-01-08
Active task :active, des2, 2014-01-09, 3d
Future task : des3, after des2, 5d
Future task2 : des4, after des3, 5d
Node
npm install cmder → Install Cmder
Git (WIP)
Everything (mostly) Git
-
git cherry-pickgit cherry-pick commit-SHAMerges a particular commitgit cherry-pick first-commit-SHA-in-range^..last-commit-SHA-in-rangeMerges a range of commits including the first in range- In
git cherry-pick A..B, A should be older than B
- In
git cherry-pick first-commit-SHA-in-range..last-commit-SHA-in-rangeMerges a range of commits NOT including the first in range
-
Stash specific file:
git stash push -m "message" <file> -
Git Commit types (not strict):
- feat: The new feature you're adding to a particular application
- fix: A bug fix
- style: Feature and updates related to styling
- refactor: Refactoring a specific section of the codebase
- test: Everything related to testing
- docs: Everything related to documentation
- chore: Regular code maintenance.[ You can also use emojis to represent commit types]
-
Git Commit Example:
type(scope): subjectfrom Art of Writing a Good Commit Message - Dev
-
- Also, WIP: Work in progress, sort of an overarching miscellaneous
-
For accidental merges done on local and NOT pushed:
- git reset --merge HEAD~1 (go back one commit on current branch)
- OR
- git fetch --all (gather all changes)
- git reset --hard origin/master (go back to current place/commit on origin/master)
-
Between git fetch and git pull, git fetch is the safe way to check out what is happening in the remote repo
-
Git File Sync Issue Troubleshooting
git rev-parse HEAD- Check current commit hashgit ls-tree -r <commit-hash>- Check ALL files associated with that particular commitgit update-index --assume-unchanged- Checks index of what you are building into your next commit (starts off as fresh and not different from previous commit) - This is the "index copy", which can be overwritten, unlike the "commit copy" of the file(s)- You essentially have three different copies of the same file as a norm: HEAD, index, and work-tree
Branching Procedures
flowchart LR
A([Master/Main]) ==> B[Main Commit];
A -. Create branch to start Feature .-> D[Feature Commit #1];
B ==> C{{Main Tip}};
D -.-> E[Feature Commit #2];
E -.-> F{{Feature Tip}};
C == No Changes ==> G((New Merge Commit));
F -- Merge into Master/Main --> G
Dev Tools
[].forEach.call($$("*"),function(a){a.style.outline="1px solid #"+(~~(Math.random()*(1<<24))).toString(16)})Input in console: Helpful for checking element layouts
Bookmarklets (WIP)
- [Get window inner width](javascript: void(0); alert(innerWidth);)
- [Get window inner height](javascript: void(0); alert(innerHeight);)
-
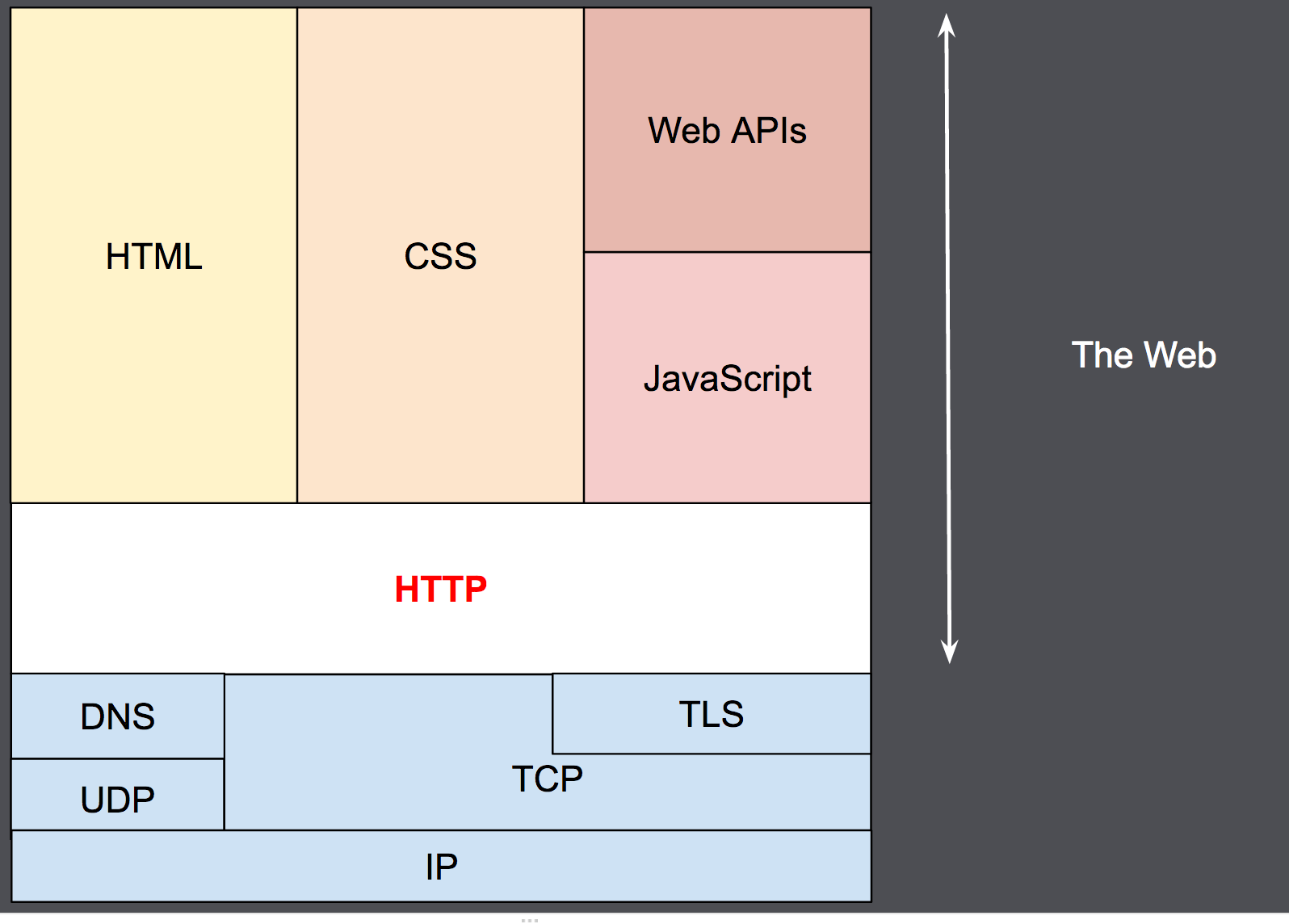
How a page is served also What is a Nameserver?
- Type URL, press Enter
- Browser uses DNS to retrieve Domain's nameservers
- Browser sends request to the Domain's nameservers for the record (DNS record) containing the IP Address of the web server
- The nameservers respond back with the IP Address of the website's server
- Browser requests website content from the IP Address
- Browser retrieves the content and renders it
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Overview
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Overview
- Most use cases implement nameservers/DNS records to point domain towards hosting
- IMPORTANT: If you change your domain’s nameservers away from the default nameservers at your domain registrar, you’ll control your domain’s DNS records at your nameserver provider.
- You can identify which nameservers are being used via a lookup tool like Whois.com or you can use the following command line options:
- Powershell:
nslookup(enter) >set q=ns(enter) - Terminal:
host -t NS exampledomain.com
- Powershell:
- Information on Subnetworks
* Side project
Hueso
Row
| M → L | B | M → T | B | M → L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 to 4 | 1 | 1 to 2 | 1 | 1 to 4 |
Tips
Very Basic Sass Filing and Article on Sass Filing with more complex suggestions
_base.scss
_layout.scss
_components.scss
main.scss
Padding/Margin/Layout
Troubleshooting Code
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner1">
<div class="inner2">
<p class="par1">Paragraph One</p>
<p class="par2">Paragraph Two</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
.outer {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
width:100vw;
z-index: 3;
background-color: hsla(200, 90%, 35%, 0.4);
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
-moz-box-sizing: border-box;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.inner1 {
height: 20vw;
width:20vw;
z-index: 1;
background-color: hsla(0, 80%, 45%, 0.4);
}
.inner1:before {
content: "Inner (ONE)";
position: absolute;
left: 30%;
top: 35%;
background-color: hsla(0, 80%, 45%, 0.4);
height: fit-content;
width: fit-content;
border-radius: 3px;
}
.inner2 {
/* box-sizing: border-box; */
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
z-index: 2;
background-color: hsla(0, 0%, 0%, 0.3);
padding: 15px 15px;
margin: 30px 30px;
}
.inner2:before {
content: "Inner (TWO)";
position: absolute;
left: 30%;
top: 40%;
background-color: hsla(0, 0%, 0%, 0.3);
height: fit-content;
width: fit-content;
border-radius: 3px;
}
.inner2 > p {
/* padding: 0; */
margin: 0;
background-color: hsla(0, 99%, 99%, 0.6);
}
.par1 {
height: 5vh;
width: 100%;
}
.inner2 > p.par1 {
margin-bottom: 5vh;
}
.par2 {
height: 10vh;
width: 100%;
}
</style>
- Gather information we need (ex. related cogs and details on progress)
- Provide updates on issues, pending projects
- Explain current projects and statuses on those projects
- Talk about time off requests
- Time Approvals -> Should be completed before EOD Thursdays