Installation Guide | readthedocs | Introduction on Binder | HowToFit
PyAutoFit is a Python-based probabilistic programming language which:
- Makes it simple to compose and fit mult-level models using a range of Bayesian inference libraries, such as emcee and dynesty.
- Handles the 'heavy lifting' that comes with model-fitting, including model composition & customization, outputting results, model-specific visualization and posterior analysis.
- Is built for big-data analysis, whereby results are output as a sqlite database which can be queried after model-fitting is complete.
PyAutoFit supports advanced statistical methods such as massively parallel non-linear search grid-searches, chaining together model-fits and sensitivity mapping.
The following links are useful for new starters:
- The introduction Jupyter Notebook on Binder, where you can try PyAutoFit in a web browser (without installation).
- The PyAutoFit readthedocs, which includes an installation guide and an overview of PyAutoFit's core features.
- The autofit_workspace GitHub repository, which includes example scripts and the HowToFit Jupyter notebook tutorials which give new users a step-by-step introduction to PyAutoFit.
PyAutoFit began as an Astronomy project for fitting large imaging datasets of galaxies after the developers found that existing PPLs (e.g., PyMC3, Pyro, STAN) were not suited to the model fitting problems many Astronomers faced. This includes:
- Efficiently analysing large and homogenous datasets with an identical model fitting procedure, with tools for processing the large libraries of results output.
- Problems where likelihood evaluations are expensive (e.g. run times of days per model-fit), necessitating highly customizable model-fitting pipelines with support for massively parallel computing.
- Fitting many different models to the same dataset with tools that streamline model comparison.
If these challenges sound familiar, then PyAutoFit may be the right software for your model-fitting needs!
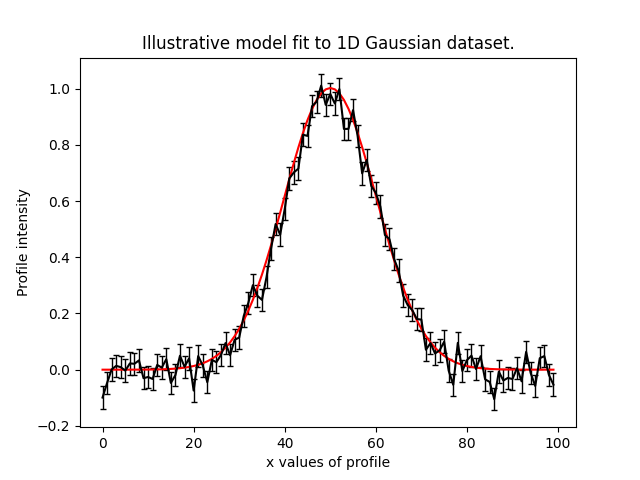
To illustrate the PyAutoFit API, we'll use an illustrative toy model of fitting a one-dimensional Gaussian to
noisy 1D data. Here's the data (black) and the model (red) we'll fit:
We define our model, a 1D Gaussian by writing a Python class using the format below:
class Gaussian:
def __init__(
self,
centre=0.0, # <- PyAutoFit recognises these
intensity=0.1, # <- constructor arguments are
sigma=0.01, # <- the Gaussian's parameters.
):
self.centre = centre
self.intensity = intensity
self.sigma = sigma
"""
An instance of the Gaussian class will be available during model fitting.
This method will be used to fit the model to data and compute a likelihood.
"""
def profile_from_xvalues(self, xvalues):
transformed_xvalues = xvalues - self.centre
return (self.intensity / (self.sigma * (2.0 * np.pi) ** 0.5)) * \
np.exp(-0.5 * (transformed_xvalues / self.sigma) ** 2.0)PyAutoFit recognises that this Gaussian may be treated as a model component whose parameters can be fitted for via a non-linear search like emcee.
To fit this Gaussian to the data we create an Analysis object, which gives PyAutoFit the data and a
log_likelihood_function describing how to fit the data with the model:
class Analysis(af.Analysis):
def __init__(self, data, noise_map):
self.data = data
self.noise_map = noise_map
def log_likelihood_function(self, instance):
"""
The 'instance' that comes into this method is an instance of the Gaussian class
above, with the parameters set to values chosen by the non-linear search.
"""
print("Gaussian Instance:")
print("Centre = ", instance.centre)
print("Intensity = ", instance.intensity)
print("Sigma = ", instance.sigma)
"""
We fit the ``data`` with the Gaussian instance, using its
"profile_from_xvalues" function to create the model data.
"""
xvalues = np.arange(self.data.shape[0])
model_data = instance.profile_from_xvalues(xvalues=xvalues)
residual_map = self.data - model_data
chi_squared_map = (residual_map / self.noise_map) ** 2.0
log_likelihood = -0.5 * sum(chi_squared_map)
return log_likelihoodWe can now fit our model to the data using a non-linear search:
model = af.Model(Gaussian)
analysis = Analysis(data=data, noise_map=noise_map)
emcee = af.Emcee(nwalkers=50, nsteps=2000)
result = emcee.fit(model=model, analysis=analysis)The result contains information on the model-fit, for example the parameter samples, maximum log likelihood
model and marginalized probability density functions.
Support for installation issues, help with Fit modeling and using PyAutoFit is available by raising an issue on the GitHub issues page.
We also offer support on the PyAutoFit Slack channel, where we also provide the latest updates on PyAutoFit. Slack is invitation-only, so if you'd like to join send an email requesting an invite.